Water, the elixir of life, covers over 70% of our planet’s surface and sustains all forms of life. However, this invaluable resource is under threat from various forms of pollution, with water pollution being one of the most significant challenges we face today. From industrial waste to agricultural runoff, the sources of water pollution are diverse and widespread. Posing grave risks to ecosystems, human health, and the economy. In this article, we delve into the complex issue of water pollution. Exploring its causes, impacts, and the urgent need for effective solutions.
Understanding Water Pollution
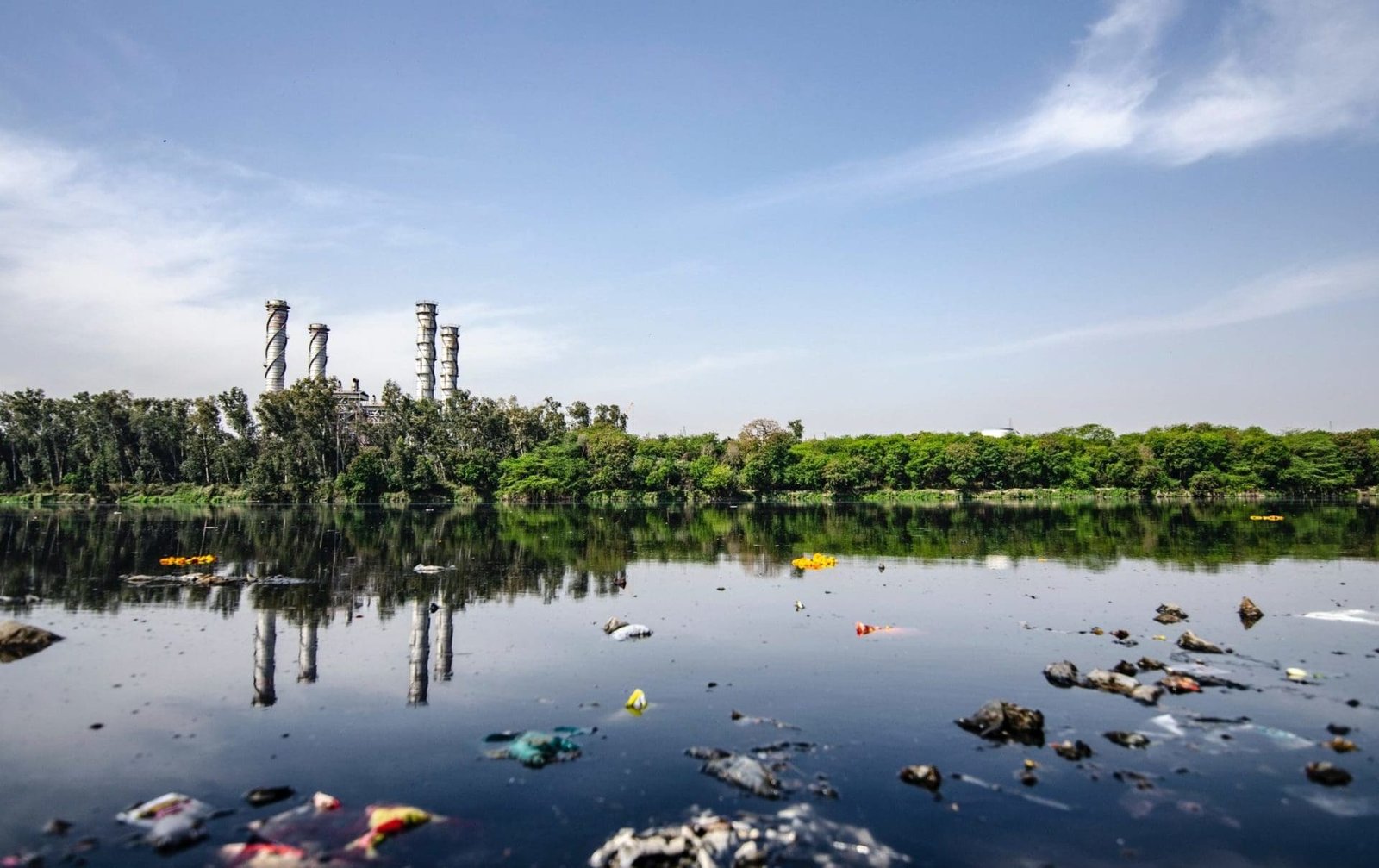
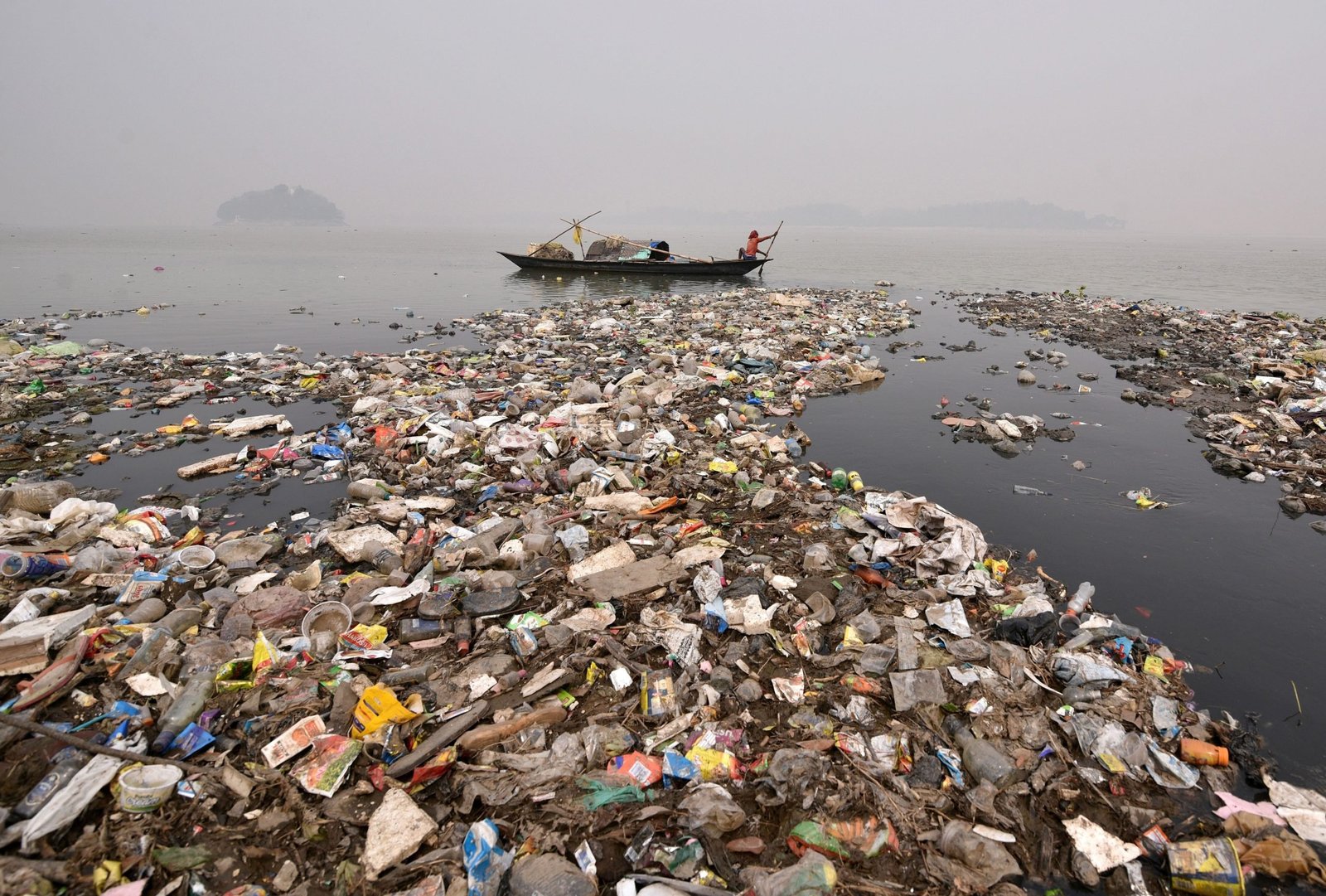
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater, with harmful substances. These contaminants can originate from various sources, including industrial activities, urban runoff, agricultural practices, and improper waste disposal. Common pollutants include chemicals, heavy metals, pathogens, and excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus.
Sources of Water Pollution
- Industrial Discharges: Industries release a wide range of pollutants into water bodies through their effluents. These pollutants can include heavy metals like mercury and lead, as well as toxic chemicals such as pesticides. Solvents, and petroleum products. Improper disposal practices and inadequate treatment of industrial wastewater exacerbate the problem.
- Agricultural Runoff: Agricultural activities contribute significantly to water pollution through the runoff of pesticides, fertilizers, and animal waste. These pollutants can contaminate surface water and seep into groundwater. Leading to eutrophication, algal blooms, and contamination of drinking water sources.
- Urbanization and Stormwater Runoff: Urban areas generate pollution through stormwater runoff, which carries contaminants such as oil, and grease. Heavy metals, and litter from streets, parking lots, and rooftops into water bodies. Urbanization also increases the load of sewage and wastewater, overwhelming treatment. Systems leading to the discharge of untreated or partially treated sewage into waterways.
Impacts of Water Pollution
- Ecological Damage: Water pollution poses grave threats to aquatic ecosystems, causing habitat destruction, declines in biodiversity, and disruptions to food chains. Contaminants can accumulate in the tissues of aquatic organisms, leading to bioaccumulation and biomagnification, with far-reaching consequences for entire ecosystems.
- Public Health Risks: Contaminated water poses significant risks to human health. Leading to waterborne diseases such as cholera, typhoid, and gastrointestinal infections. Exposure to pollutants like heavy metals and chemicals has been linked to various health problems, including cancer. Neurological disorders, and reproductive issues.
- Economic Costs: Water pollution takes a heavy toll on economies through impacts on sectors. Such as fisheries, tourism, and public health. Declines in water quality can lead to reduced fish stocks, beach closures, and the loss of recreational opportunities. Affecting local economies and livelihoods.
Challenges in Addressing Water Pollution
- Lack of Regulatory Enforcement: In many parts of the world, weak enforcement of environmental regulations allows industries and other polluters to discharge contaminants into water bodies with impunity. The absence of stringent penalties and inadequate monitoring further exacerbates the problem.
- Complexity of Pollution Sources: Addressing water pollution requires tackling a complex web of pollution sources, ranging from point sources like industrial discharge pipes to non-point sources like agricultural runoff. Coordinating efforts across multiple sectors and stakeholders presents significant challenges.
- Limited Access to Clean Water: Access to clean and safe drinking water remains a challenge for millions of people worldwide, particularly in low-income and marginalized communities. Water pollution exacerbates this problem, perpetuating cycles of poverty and inequality.
Strategies for Mitigation and Prevention
- Improved Regulation and Enforcement: Strengthening environmental regulations and ensuring their effective enforcement is crucial for preventing and controlling water pollution. Governments must establish clear standards for pollutant discharges and implement robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms to hold polluters accountable.
- Investment in Wastewater Treatment: Investing in wastewater treatment infrastructure is essential for reducing the discharge of untreated or inadequately treated sewage into water bodies. Upgrading existing treatment plants and implementing decentralized treatment systems can help improve water quality and protect public health.
- Promotion of Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices, such as precision farming and organic agriculture, can help minimize the runoff of pesticides and fertilizers into water bodies. Similarly, promoting green infrastructure in urban areas, such as rain gardens and permeable pavement, can reduce stormwater runoff and improve water quality.
Public Awareness and Community Engagement
Raising public awareness about the importance of clean water and the impacts of water pollution is crucial for fostering individual and collective action. Education campaigns, community-based monitoring initiatives, and partnerships between government, civil society, and the private sector can empower communities to protect and preserve their water resources.
In conclusion, water pollution represents a grave threat to ecosystems, human health, and the economy, requiring urgent and concerted action at local, national, and global levels. By addressing the root causes of pollution, strengthening regulatory frameworks, investing in infrastructure, and promoting sustainable practices, we can safeguard this precious resource for future generations. Only through collective efforts and a commitment to stewardship can we ensure a future where clean and safe water is accessible to all.
Internal link: ragdi.com